1.Intelligent frequency-selecting
When the current wireless ad hoc network works on a fixed frequency point, in order to avoid interference, it is necessary to manually intervene to select a relatively good frequency point for operation based on the spectrum scanning results of each node in the entire network.On the one hand, this manual intervention approach is very inefficient and requires high requirements for the user. On the other hand, due to geographical differences, it is often impossible to select a frequency point with minimal interference for networking and transmission throughout the entire network.
The adaptive intelligent frequency selection technology used in the current system performs real-time sensing and spectrum monitoring of the wireless environment across the entire network for these frequencies during operation, based on the frequency list configured during system operation. Each node intelligently and dynamically adjusts its operating frequency based on external electronic environment, interference conditions, and other factors. Each node dynamically selects an operating frequency based on the optimal receiving performance criteria.Each node is independently selected and is not dependent on each other, thus achieving intelligent dynamic heterogeneous networking, avoiding interference, and improving overall network transmission performance.The goal is to achieve optimal performance across the entire network.At the same time, due to the lack of human intervention, the complexity of network configuration and use is greatly reduced, enhancing network usability.
As shown in the figure below, the radios of nodes 1, 2, and 3 sense the spectrum situation in real time according to their own wireless environment, and select frequency points f1, f2, and f3 as working frequencies (f1, f2, and f3 can be the same or different, and each node selects independently without affecting each other).When nodes 2 and 3 simultaneously send data to node 1, frequency point f1 is used.When nodes 1 and 3 send data to node 2, frequency point f2 is used.When nodes 1 and 2 send data to node 3, frequency point f3 is used.When there are more than three nodes, the system adopts the same rules.In summary, each node intelligently and dynamically adjusts its own frequency point without affecting each other or relying on each other. Therefore, in the MESH network, the frequency points used in the bidirectional links between each node are different, achieving optimal anti-interference performance.This function is completely automated by the system based on algorithms, and it is adjusted in real time according to the external wireless environment and spectrum detection situation, without manual operation, making it simple and easy to use.
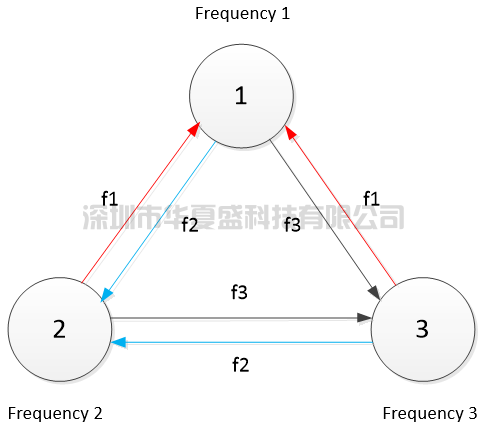
In practical applications, it is almost impossible for all nodes to have the same interference situation and the same frequency point is the optimal receiving frequency point.Therefore, compared to other brands' interference avoidance technology (Inference Avoidance, when the MESH network is working at a certain frequency point, the whole network will switch to another frequency point), SINOSUN MimoMesh's intelligent frequency selection technology performs better in terms of robustness, ease of use, anti-interference ability, and transmission performance, easily maintaining the optimal quality of the MESH link and keeping the transmission performance at its best.
2.Enhanced intelligent frequency-selectting
All monitoring and frequency adjustment work in ordinary intelligent frequency selection technology is based on a preconfigured frequency list, so the selection of the frequency list is very important.However, because the frequency list is selected and configured by humans, if the selection of the frequency list is not good, it will also affect the overall system performance.
The enhanced intelligent frequency selection technology can effectively solve the above problems. This technology no longer relies on existing frequency lists, but instead uses a smaller frequency step (such as 1 MHz) within the frequency bands supported by the hardware (the actual frequency bands are determined by the specific hardware), while working in the MESH mode, to perform real-time spectrum monitoring of the electromagnetic environment, and thus select the optimal operating frequency point.
Each node intelligently and dynamically selects its own operating frequency within the full frequency band based on external electromagnetic environment, interference conditions, and other factors, with the optimal receiving performance as the criterion. The nodes do not affect each other, thus achieving dynamic inter-frequency networking within the full frequency band, avoiding interference, improving overall network transmission performance, further reducing network configuration and complexity, and enhancing system usability.
In terms of networking logic and functional performance, enhanced intelligent frequency selection technology is basically the same as intelligent frequency selection technology. The biggest improvement of the former is that it can more accurately detect, scan and analyze the entire frequency band, with stronger adaptability to complex environments and better performance. At the same time, it further optimizes the sending mechanism of control information and data information, improving the anti-interference ability and enhancing the robustness of the MESH system in complex electromagnetic environments.
3.Frequency Hopping
High-speed frequency hopping is also a conventional anti-interference method that can greatly reduce the risk of being captured, tracked, and detected compared to other methods, effectively countering interference methods such as tracking-based interference.
The current MESH system supports a frequency hopping rate of no less than 1000 hops per second, with a maximum of 256 frequency hopping points. The relevant frequency hopping patterns have been fully randomized. At the same time, by increasing the complexity of the frequency hopping pattern, lengthening the repetition period, and enhancing the flexibility of the frequency hopping networking pattern, the difficulty of deciphering the frequency hopping pattern by the enemy can be greatly increased, effectively reducing the risk of malicious interference to the MESH system.
4.Adaptive intelligent frequency hopping
When conventional frequency hopping technology is subject to widespread interference in a MESH network, the system has a high probability of interruption and an increased error rate, resulting in a significant reduction or even interruption of service transmission capabilities.The introduction of adaptive frequency hopping technology can effectively improve this situation, further enhancing the anti-interference capabilities of the MESH system, ensuring the transmission capability of MESH data services under widespread interference.
Adaptive frequency hopping technology adds dynamic real-time spectrum monitoring to the entire MESH network while performing high-speed frequency hopping. It relies on existing frequency hopping point lists or on hardware-supported frequency bands (depending on the hardware) to perform real-time sensing and spectrum monitoring of the entire frequency band with a small frequency step (such as 1 MHz).Each node intelligently selects several optimal frequency points to form a frequency hopping frequency set based on real-time spectrum monitoring results, external electromagnetic environment, and interference conditions, achieving intelligent, dynamic, and different frequency hopping networking, effectively avoiding interference while hopping at high speed.
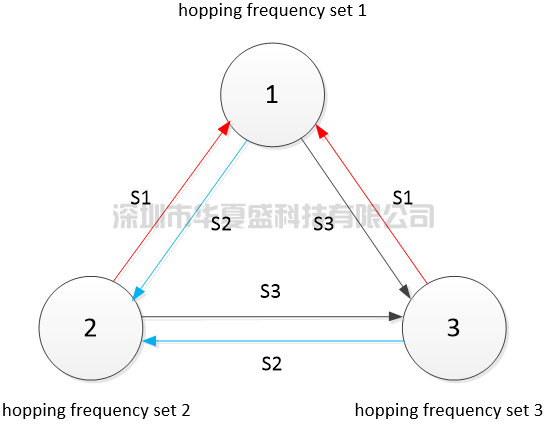
As shown in the figure below, nodes 1, 2, and 3 select subsets S1, S2, and S3 from all available frequency sets as the frequency hopping set according to their real-time electromagnetic environment sensing and spectrum monitoring conditions (the elements of the three sets S1, S2, and S3 can be the same or different, and each node independently selects frequency points without affecting each other).
When nodes 2 and 3 send data to node 1, they use frequency set S1 to transmit data by frequency hopping.When nodes 1 and 3 send data to node 2, they use frequency set S2 to transmit data by frequency hopping.When nodes 1 and 2 send data to node 3, they use frequency set S3 to transmit data by frequency hopping.When there are more than 3 nodes, the system logic is the same.In short, due to the intelligent adjustment of each node's own frequency hopping set, the frequency hopping set used by the bidirectional links between each frequency point in the entire MESH network is also different.This function is completely automated by the system, without manual intervention, making it simple and easy to use.It enhances the anti-interference ability and reliability of the MESH system.
5.Dynamic adaptive anti-jamming
In complex electromagnetic environments, in order to improve the overall reliability of the MESH system and ensure the transmission of data services in the MESH link, while using all the above-mentioned frequency hopping, intelligent frequency selection, and other technologies, the MESH system also has the ability to dynamically adapt to interference.
In the data transmission link between any two nodes, the receiving end will collect real-time statistics such as signal-to-noise ratio, error rate, and many other information. Based on these information, the system will select the optimal modulation and coding format and related retransmission strategies according to the algorithm, and feedback the corresponding results to the sending end. The sending end will adjust the sending strategy again according to the feedback information (dynamically adjust the transmission channel redundancy), thus achieving dynamic adaptive anti-interference.
Through dynamic adaptive anti-interference technology, the MESH system can ensure maximum transmission efficiency and obtain optimal transmission capacity when it is not interfered.Conversely, when it is interfered, it can effectively combat the impact of interference, sacrificing some efficiency while trying to ensure the integrity of data services and ensure reliable transmission of services.
Currently, the MESH system supports four different anti-interference modes, corresponding to four different data insertion, detection, and processing capabilities with maximum link bandwidth redundancy:1) Anti-interference level 1: When the channel resources (time or frequency band) are within 15% of interference, normal communication and data transmission can be guaranteed;2) Anti-interference level 2: When channel resources (time or frequency band) are within 30% of interference, normal communication and data transmission can be guaranteed;3) Anti-interference level 3: When the channel resources (time or frequency band) are within 50% of interference, normal communication and data transmission can be guaranteed;4) Anti-interference level 4: When the channel resources (time or frequency band) are within 70% of interference, normal communication and data transmission can be guaranteed.

